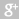Pipe for floor heating PE-RT cross-linked polyethylene
| Price: | 6.80 UAH |
| Company: | Dongorplast |
| Seller: |  Dongorplast Natal'ya Dongorplast Natal'ya |
| Phones: |  +380504793010 Show phone |
| Address: | Ukraine, Donets'ka Oblast', Donetsk |
Pipes made of cross linked polyethylene characterized by the following properties:
•high
fatigue strength even at elevated temperatures (up to 110° C);
•exceptional dimensional stability
(without application of the load, the material is not deformed up to 200° C);
•crack resistance;
•high impact and shock
viscosity in places cuts even at temperatures below -50° C;
•optimal balance of flexibility and
strength;
•high wear resistance on
abrasion and cut;
•excellent shrinkage properties;
•high resistance to impact
chemical reagents;
•the absence of heavy metal ions
and halogen;
•resistance to corrosion;
•potential lifetime
pipes for over 50 years at a constant temperature of 70° C.
Thermal properties
Due to the formation of cross-links also improves the behavior of the material at low temperature. Because cross-linked polyethylene is not such brittle, it can be used, depending on the mechanical load temperature range from -120° to +120° C. cross-linked polyethylene for a small period of time can withstand without mechanical load temperature to +120° C.
Mechanical properties
Mechanical properties of cross-linked polyethylene are direct dependence on temperature.
As mentioned above, in the process of blending under high pressure decreases the crystallinity of the starting material. Due to this is especially flexible material that does not break even after repeated bending.
Fire
Cross-linked polyethylene is a pure hydrocarbon polymer and therefore flammable. Calipatria when burning inherent seamless polyethylene, cross-linked polyethylene is slowing down. The material begins to flow drop by drop only when it is heated to temperatures above 400° C (the temperature of dissolution). In the the decay reaction formed pure water and carbon dioxide, which do not cause corrosion and are not poisonous.
Resistance to chemical
reagents
Good stability of macromolecular source material to chemical reagents further increases in the process of polymer crosslinking. Cross-linked polyethylene is resistant to normal solvents: aliphatic (e.g., gasoline), aromatic (e.g., toluene) and chlorinated hydrocarbons (e.g. trichloroethylene). Under the influence of volatile ingredients organic compounds (fats, oils, waxes) material little swells. Compared with unstitched the high density polyethylene sewn polyethylene is more resistant to high temperature. Strong oxidizing agents, for example, nitric acid or halogen, corroding material. Pipes made of cross linked polyethylene particularly tensile strength compared to other polyolefins. Contact with detergent additives, conventional antifreeze and protection from corrosion does not lead to the formation of cracks.
Changing the properties of polymers in contact with the chemical reagents based primarily on physical processes, for example, the swelling or dissolution of the polymers. Cross-linked polyethylene behaves thanks the crosslinking is much better than the types of polyethylene without cross-linking. To assess the stability was considered changing properties stretching during storage of the material in the appropriate chemical environment without additional application of mechanical forces. In this table information about resistance to the effects of various chemical reagents cannot formally transferred to the behaviour of the pipe filled with the appropriate substance, and under pressure. Here the so-called necessary research prototypes tubes for durability.
The manufacturing process
The source material is polyethylene with a large molecular weight and high density. Polyethylene is formed by polymerization of ethylene is a gaseous product consisting solely of carbon atoms (C) and hydrogen (H). As a result of polymerization